Cell Therapy


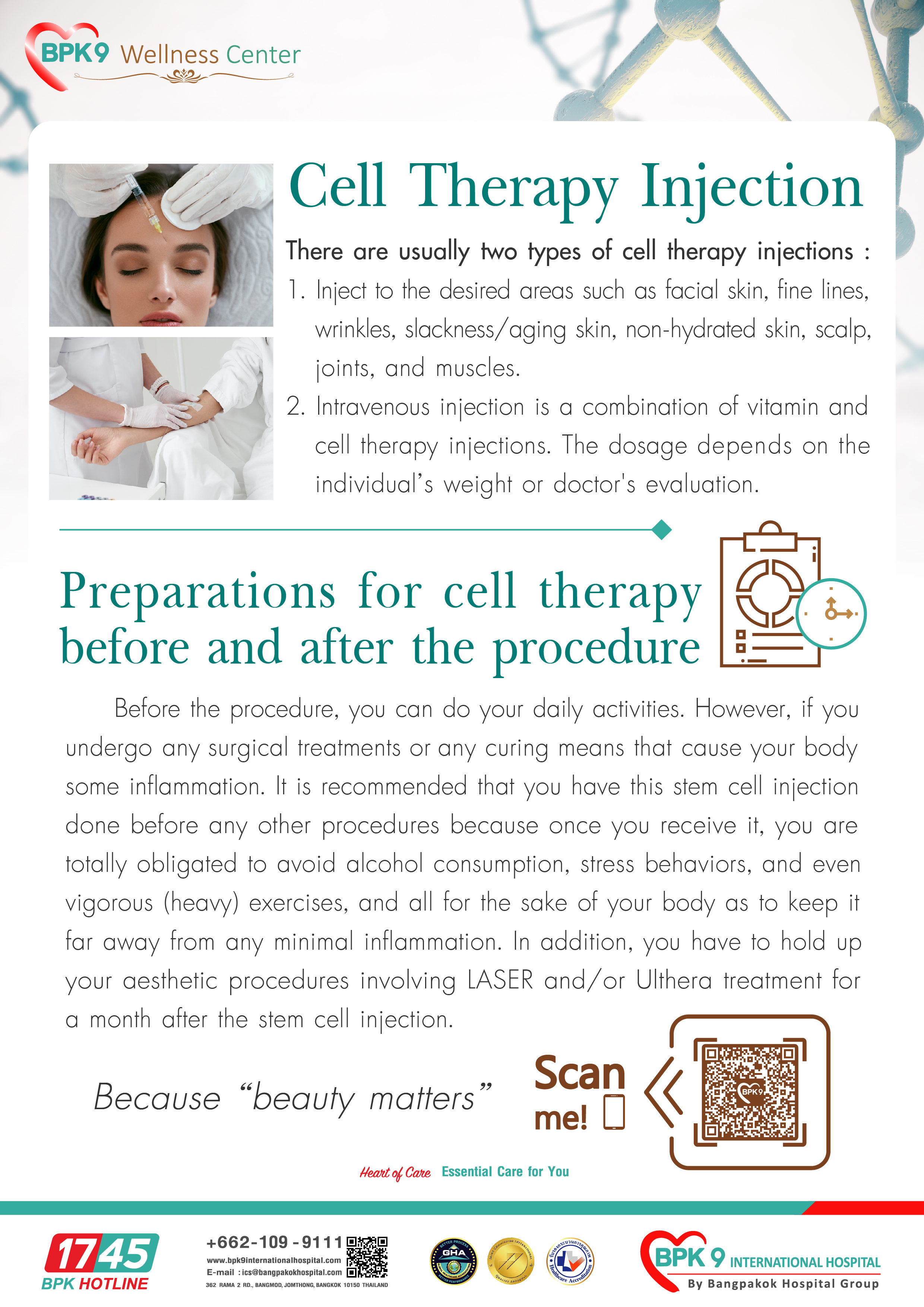
Cell Therapy and Its Anti-Aging Potential: Unlocking the Fountain of Youth
Aging is a natural process, but for centuries, humanity has searched for ways to slow its pace and preserve vitality. Today, scientific innovation is bringing us closer to this dream, and at the heart of it is cell therapy, a cutting-edge approach that holds remarkable promise in the field of anti-aging.
Cell therapy involves the administration of live cells into the body to repair, replace, or regenerate damaged tissues and restore normal function. While originally developed to treat conditions like blood disorders, immune deficiencies, and certain cancers, researchers have increasingly turned their attention to the anti-aging potential of cell therapy.
How Does Cell Therapy Work against Aging?
As we age, our cells gradually lose their ability to divide, repair, and regenerate. Skin becomes thinner, muscles weaken, organ function declines, and the immune system slows down. Cell therapy addresses this at the very root — the cellular level.
By introducing young, healthy cells or stem cells into the body, cell therapy can:
- Stimulate tissue regeneration: Replace damaged or aged cells with new ones, rejuvenating skin, muscles, and organs.
- Reduce inflammation: Chronic inflammation accelerates aging. Certain cell types can dampen inflammatory responses, promoting healthier aging.
- Enhance immune function: Cell therapy can help restore immune balance, improving resilience against infections and age-related diseases.
- Boost collagen and elastin production: In cosmetic applications, stem cells can stimulate the production of skin-firming proteins, reducing wrinkles and improving skin texture.
The Science behind the Promise
The magic of cell therapy lies in stem cells, particularly mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), which have the remarkable ability to differentiate into a variety of cell types — from bone and cartilage to fat and muscle. When introduced into aging tissues, these cells secrete growth factors, cytokines, and extracellular vesicles that orchestrate repair and regeneration.
Clinical studies and early trials have shown encouraging results. For example, patients receiving stem cell infusions have reported improved skin elasticity, reduced fine lines, enhanced energy levels, and even improved cognitive function. While more research is needed, the potential is undeniably exciting.
A Glimpse Into the Future
The future of anti-aging cell therapy is incredibly promising. As science advances, we may soon see personalized cell therapies tailored to an individual’s unique genetic and biological profile, offering unprecedented levels of rejuvenation.
However, it’s important to approach this field with balanced optimism. Ethical, safety, and regulatory considerations remain critical. Only therapies developed through rigorous clinical testing should be considered to ensure both safety and efficacy.

